Biosphere Reserves in India
- 23 Jan 2020
- 8 min read
Last Updated: September 2022
For Prelims: Biosphere Reserve, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), Biosphere Reserves in India, Man and Biosphere Programme.
For Mains: Biosphere Reserves: Criteria for Designation, Main Zones, Functions, International Status.
What is Biosphere Reserve?
- Biosphere Reserve (BR) is an international designation by United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) for representative parts of natural and cultural landscapes extending over large areas of terrestrial or coastal/marine ecosystems or a combination of both.
- Biosphere Reserves tries to balance economic and social development and maintenance of associated cultural values along with the preservation of nature.
- Biosphere Reserves are thus special environments for both people and nature and are living examples of how human beings and nature can co-exist while respecting each other’s needs.
What are the Criteria for Designation of Biosphere Reserve?
- A site must contain a protected and minimally disturbed core area of value of nature conservation.
- The core area must be a bio-geographical unit and should be large enough to sustain a viable populations representing all trophic levels.
- The involvement of local communities and use of their knowledge in biodiversity preservation.
- Area’s potential for preservation of traditional tribal or rural modes of living for harmonious use of the environment.
What are the Three Main Zones of Biosphere Reserve?
- Core Areas:
- It is the most protected area of a biosphere reserve. It may contain endemic plants and animals.
- They conserve the wild relatives of economic species and also represent important genetic reservoirs having exceptional scientific interest.
- A core zone is a protected region, like a National Park or Sanctuary/protected/regulated mostly under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972. It is kept free from human interference.
- Buffer Zone:
- The buffer zone surrounds the core zone, and its activities are managed in this area in ways that help in the protection of the core zone in its natural condition.
- It includes restoration, limited tourism, fishing, grazing, etc., which are permitted to reduce its effect on the core zone.
- Research and educational activities are to be encouraged.
- Transition Zone:
- It is the outermost part of the biosphere reserve. It is the zone of cooperation where human ventures and conservation are done in harmony.
- It includes settlements, croplands, managed forests and areas for intensive recreation and other economic uses characteristics of the region.

What are the Functions of Biosphere Reserve?
- Conservation:
- Managing Biosphere Reserve’s genetic resources, endemic species, ecosystems, and landscapes.
- It may prevent man-animal conflict eg., death of tiger Avni who was shot dead when she turned man-eater
- Along with the wildlife, culture and customs of tribals are also protected
- Development:
- Promoting economic and human growth that is sustainable on a sociocultural and ecological level. It seeks to strengthen the three pillars of sustainable development: social, economic and protection of the environment.
- Logistic support:
- Promoting research activities, environmental education, training and monitoring in the context of local, national and international conservation and sustainable development.
How many Biosphere Reserves are in India?
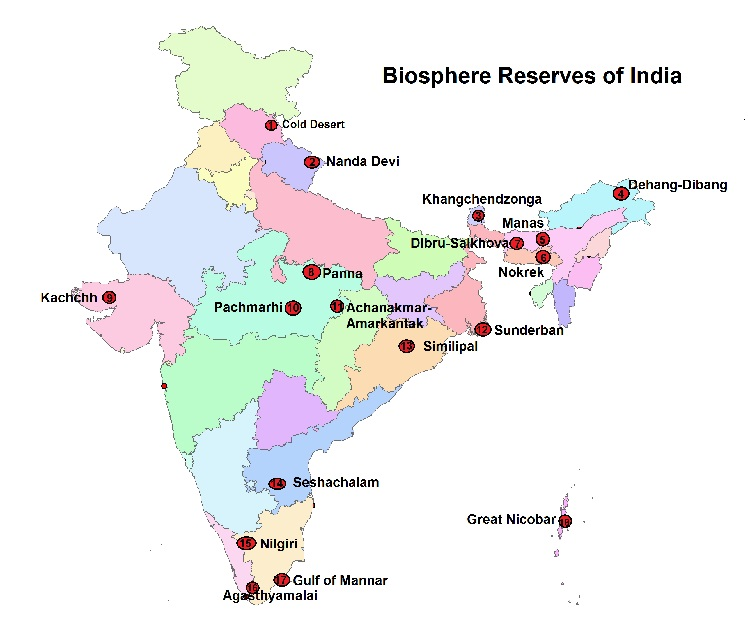
- There are 18 biosphere reserves in India:
- Cold Desert, Himachal Pradesh
- Nanda Devi, Uttrakhand
- Khangchendzonga, Sikkim
- Dehang-Debang, Arunachal Pradesh
- Manas, Assam
- Dibru-Saikhowa, Assam
- Nokrek, Meghalaya
- Panna, Madhya Pradesh
- Pachmarhi, Madhya Pradesh
- Achanakmar-Amarkantak, Madhya Pradesh-Chhattisgarh
- Kachchh, Gujarat (Largest Area)
- Similipal, Odisha
- Sundarban, West Bengal
- Seshachalam, Andhra Pradesh
- Agasthyamala, Karnataka-Tamil Nadu-Kerala
- Nilgiri, Tamil Nadu-Kerala (First to be Included)
- Gulf of Mannar, Tamil Nadu
- Great Nicobar, Andaman & Nicobar Island
What is the International Status of Biosphere Reserve?
- UNESCO has introduced the designation ‘Biosphere Reserve’ for natural areas to minimize conflict between development and conservation.
- Biosphere Reserves are nominated by national government which meets a minimal set of criteria under the Man and Biosphere Reserve Program of UNESCO.
- There are currently 738 biosphere reserves in 134 countries, including 22 transboundary sites.
- There are total 12 biosphere reserves of India which have been recognized internationally under Man and Biosphere Reserve program:
- Nilgiri (First to be included)
- Gulf of Mannar
- Sunderban
- Nanda Devi
- Nokrek
- Pachmarhi
- Similipal
- Achanakmar – Amarkantak
- Great Nicobar
- Agasthyamala
- Khangchendzonga (Added under Man and Biosphere Reserve Program in 2018)
- Panna, Madhya Pradesh (The latest included BR)
What is Man and Biosphere Programme?
- Launched in 1971, UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB) is an intergovernmental scientific programme that aims to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of relationships between people and their environments.
- MAB combines natural and social sciences, economics and education to improve human livelihoods and the equitable sharing of benefits, and to safeguard natural and managed ecosystems, thus promoting innovative approaches to economic development that are socially and culturally appropriate, and environmentally sustainable.
What is Biosphere Conservation?
- A scheme called Biosphere Reserve is being implemented by the Government of India since 1986, in which financial assistance is given in 90:10 ratio to the Northeastern Region States and three Himalayan states and in the ratio of 60:40 to other states for maintenance, improvement, and development of certain items.
- The State Government prepares the Management Action Plan which is approved and monitored by the Central MAB Committee.
What can be the Way Forward?
- Land rights of tribals which depend on the forest resources in transition areas must be secured.
- Resources like spices from the reserves of Kerala should be marketed with “Biosphere Reserve Tags” which will increase their value.
- Munnar declaration which suggests that biosphere reserves can be carved out of the desert and Gangetic plain bio-geographic zones should also be implemented.
- As the biosphere reserve concept was aimed at sustainable development, the term, reserve, should be replaced with a suitable word.
- The government must take strict steps against alien species invading various biosphere reserves e.g., Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. The most important strategy for the conservation of biodiversity together with traditional human life is the establishment of (2014)
(a) biosphere reserves
(b) botanical gardens
(c) national parks
(d) wildlife sanctuaries
Ans: (a)